414. Equation
The positive
integer n is given. How many
solutions in positive integers have the next equation:
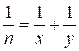
Input. One integer n
(1 ≤ n ≤ 109).
Output. The number of
solutions in positive integers for the given equation.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
2 |
3 |
SOLUTION
mathematics
Algorithm analysis
The equation  is equivalent to
is equivalent to  ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]()
The number of
solution pairs (x, y) equals to the number of ways to
represent number n2 as a
product of two factors. This, in turn, equals to the number of divisors for the
value of n2.
If n = ![]() , the number of its divisors equals to
, the number of its divisors equals to
d(n) = (a1 + 1) * (a2
+ 1) * … * (ak + 1)
The answer is the
value d(n2) = (2a1 + 1) * (2a2 + 1) * … * (2ak + 1).
Example
For n = 2 we have: d(22) = 2 * 1 + 1 = 3.
For n = 12 factorization is 12 = 22 * 3. So
d(122) = (2 * 2 + 1)
* (2 * 1 + 1) = 5 * 3 = 15
Number 122 for example can be
represented in the form 4 * 36. Let’s solve the system of equations:
 ,
, 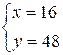
One of solutions of
original equation is ![]() .
.
Algorithm realization
Read the input
data. Initialize the current answer of the problem res with one.
scanf("%d",&n);
res = 1;
For each
prime divisor i of number n calculate the degree c, with which it is included in n. Multiply the result res by 2 * c + 1.
for(i = 2; i <= sqrt(n); i++)
{
c = 0;
while (n % i == 0)
{
n /= i; c++;
}
res = res * (2 * c
+ 1);
}
If n > 1 at the end of the loop, it equals to
the prime divisor of input number n. This
divisor enters into n with degree 1, so
we need to multiply res by 2 * 1 + 1
= 3.
if (n > 1) res *= 3;
Print the
answer.
printf("%d\n",res);
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int res = 1, n = con.nextInt();
for(int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n);
i++)
{
int c;
for(c = 0; n % i == 0; c++) n /= i;
res = res * (2 * c + 1);
}
if (n > 1) res *= 3;
System.out.println(res);
}
}
Python realization
import math
n = int(input())
res = 1
for i in range(2, int(math.sqrt(n)) + 1):
c = 0;
while n % i == 0:
n = n // i
c += 1
res = res * (2 * c + 1)
if n > 1: res *= 3
print(res)